Risk of error estimated from Palestine pharmacists’ knowledge and certainty on the adverse effects and contraindications of active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients
Article information
Abstract
Purpose:
This study aimed to investigate community pharmacists’ knowledge and certainty of adverse effects and contraindications of pharmaceutical products to estimate the risk of error. Factors influencing their knowledge and certainty were also investigated.
Methods:
The knowledge of community pharmacists was assessed in a cross-sectional design using a multiple-choice questions test on the adverse effects and contraindications of active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients from May 2014 to March 2015. Self-rated certainty scores were also recorded for each question. Knowledge and certainty scores were combined to estimate the risk of error.
Results:
Out of 315 subjects, 129 community pharmacists (41.0%) completed the 30 multiple-choice questions test on active ingredients and excipients. Knowledge on active ingredients was associated with the year of graduation and obtaining a licence to practice pharmacy. Knowledge on excipients was associated with the degree obtained. There was higher risk of error in items on excipients than those on ingredients (P<0.01).
Conclusion:
The knowledge of community pharmacists in Palestine was insufficient with high risk of errors. Knowledge of community pharmacists on the safety issues of active ingredients and excipients need to be improved.
Introduction
Pharmaceutical products often contain both active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and inactive pharmaceutical excipients. Knowledge of community pharmacists on the safety of pharmaceutical excipients was not assessed yet in Palestine. The goals of this study were to investigate knowledge and self-rated certainty to estimate the risk of error in APIs and excipients and to explore factors influencing knowledge of community pharmacists in Palestine.
Methods
Study design
This was a cross-sectional observational study conducted from May 2014 and March 2015 in the West Bank of Palestine. Pharmacists who agreed to participate in the study gave their relevant background characteristics and performed a test composed of multiple choice questions (MCQs) on the adverse effects and contraindications of APIs and pharmaceutical excipients.
Participants
The number of pharmacies operating in the cities of the West Bank was 315. In the present study, we invited one pharmacist working in each pharmacy to participate in the study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: a pharmacist with at least a basic degree in pharmacy; licensed to practice pharmacy in Palestine, and working in a community pharmacy with at least 50% part-time job. We did not include pharmacists who worked in pharmaceutical industry, insurance companies, or hospitals.
Items and examinees’ characteristics
The study tool was a test of two sections consisting of 30 MCQ items with four options each. The test consisted of 15 items on the adverse effects and contraindications of APIs and 15 items on the adverse effects and contraindications of pharmaceutical excipients. The items were based on the European Commission Guideline on Excipients in the label and package leaflet of medicinal products for human use available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500003412.pdf
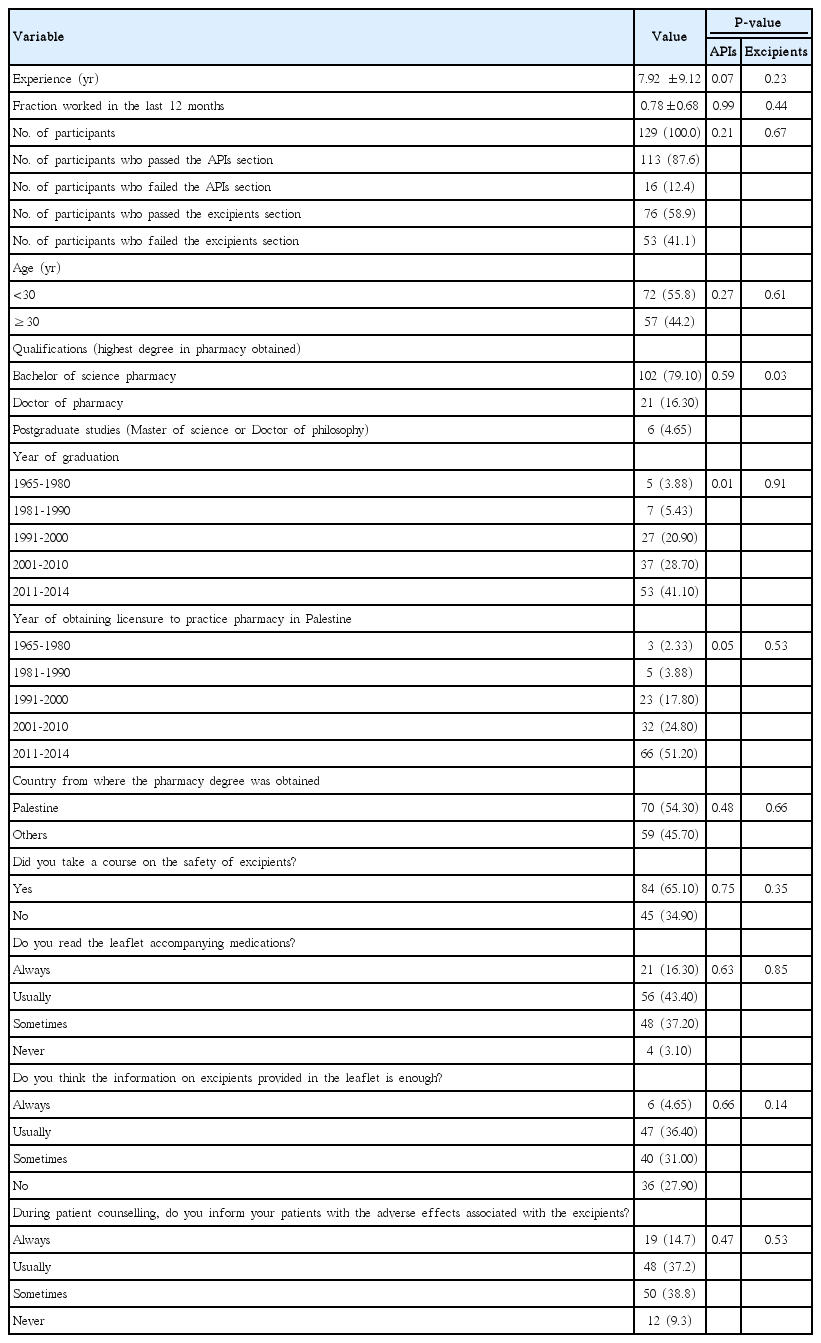
The following characteristics of examinees were recorded: gender, age, qualifications (degrees), years after graduation, university and country from where the basic pharmacy degree was earned, years after obtaining a licensure to practice pharmacy, length of work experience as a community pharmacist in at least a 50% part-time job, employment fraction in the last 12 months, and place of work (current city). Participants were asked if they studied the adverse effects of pharmaceutical excipients during their academic pharmacy courses, read the leaflets accompanying medications, informed their patients about the adverse effects of the pharmaceutical excipients when they dispensed pharmaceutical products, and if they thought the information provided by the manufacturers on the pharmaceutical excipients was sufficient.
Validity and reliability test
Seven experts with different backgrounds in pharmacy, pharmacology, pharmaceutical care, and medication errors were asked to complete the test for establishing the construct validity. The difficulty index of test items responded by seven experts was 0.943 (SD = 0.052) in the APIs section and 0.914 (SD= 0.062) in the pharmaceutical excipients section. Testing experts’ scores against pharmacists’ scores in each section using an independent t-test, experts’ scores were significantly higher in both sections (P<0.001), which indicated a valid test. The two sections of the test showed Cronbach’s alpha values of 0.53 and 0.56 and Guttman lambda values of 0.56 and 0.60 for the APIs and pharmaceutical excipients, respectively.
Certainty
Pharmacists were asked to indicate a self-rated certainty on each answered question on a Likert scale graded from 0-3, where, 0 indicated very uncertain which meant would search for help, consult colleagues/reference books, 1 indicated relatively uncertain which meant would probably search for help, 2 indicated relatively certain which meant would probably not search for help, and 3 indicated very certain which meant would not search for help.
Risk of error
Knowledge and certainty were combined for each question to estimate the risk of error rated from 1 to 3. Correct answers combined with high certainty (relatively certain and very certain, i.e., certainty score of 2 or 3) was assigned a low risk of error (score 1), low certainty (relatively uncertain and very uncertain, i.e., certainty score of 1 or 0) independent of correct answer was assigned a moderate risk of error (score 2), and incorrect answer combined with high certainty (relatively certain and very certain, i.e., certainty score of 2 or 3) was assigned as a high risk of error (score 3). Unanswered questions were considered as ‘incorrect answers,’ and unanswered certainty scores were considered as ‘very uncertain.’
Correlation between knowledge scores and certainty for active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients related questions
Knowledge and certainty scores for each participant in each question were converted into percentages. A correct answer was given a score of ‘100%’ and a wrong answer was given a score of ‘0%.’ The self-rated certainty scores were converted into percentages as follows: ‘0’ which indicated very uncertain which meant would search for help, consult colleagues/reference books= 0%, ‘1’ which indicated relatively uncertain which meant would probably search for helP=33.3%, ‘2’ which indicated relatively certain which meant would probably not search for helP=66.7%, and ‘3’ which indicated very certain which meant would not search for helP=100%. Correlation was investigated using Pearson’s correlation test.
Ethical approval
The protocol and ethics of this study were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) Committee of An-Najah National University (An-Najah IRB #03/2014).
Data analysis
Depending on the data distribution, different groups were compared using t-test/Mann-Whitney U-test, analysis of variance/Kruskal-Wallis, and Pearson tests. Knowledge on adverse effects, contraindications of APIs, and pharmaceutical excipients were compared among groups. The scores of participants in each APIs and excipients related question were compared with the arbitrary certainty scores using Mann-Whitney U-test. Two-tailed significance tests were used, and a P-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The analyses were performed using IBM SPSS ver. 21.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
Characteristics of the participants
We intended to include at least one pharmacist working in each of the 315 pharmacies in the cities of the West Bank. The total number of participants in this study was 129 pharmacists, giving a response rate of 41%. The characteristics of the study participants are summarized in Table 1.
Outcome of knowledge tests
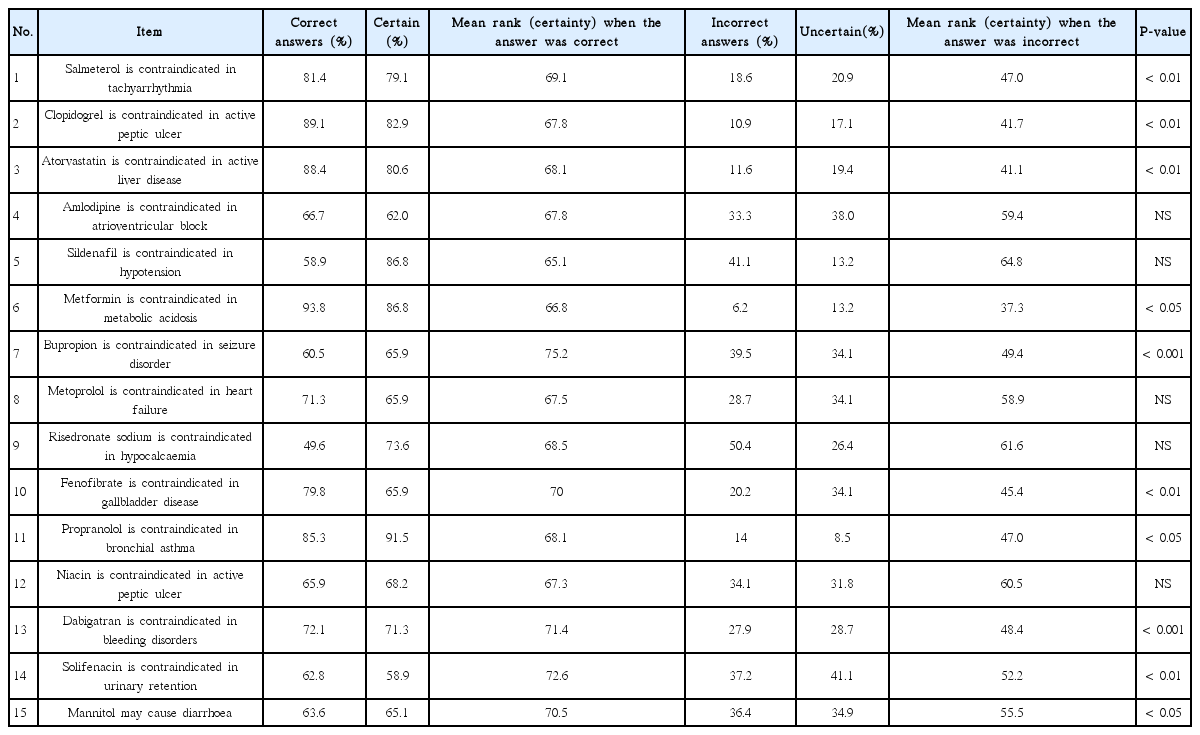
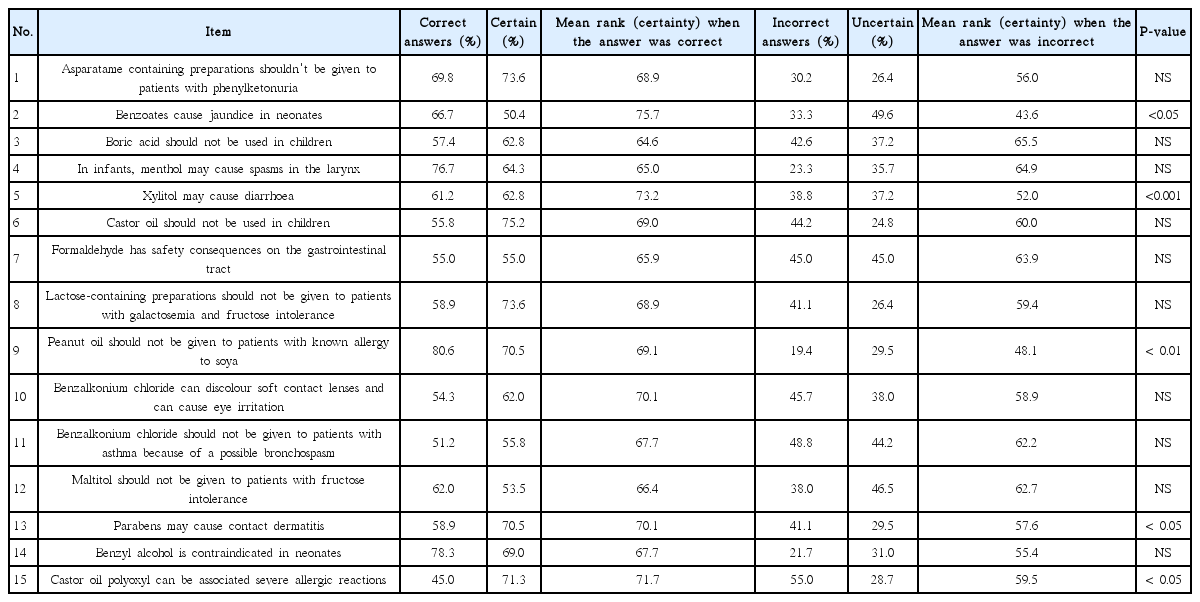
The overall outcome of the knowledge tests on the adverse effects and contraindications of APIs and pharmaceutical excipients is shown in Table 2. In general, pharmacists scored higher knowledge on APIs than that on excipients. There was modest positive correlation between the scores of participants in APIs and pharmaceutical excipients (Pearson’s r=0.353, P<0.001). Knowledge in APIs was associated with year of graduation (P<0.01) and year of obtaining licensure to practice pharmacy (P<0.05) (Table 1); while, knowledge of pharmaceutical excipients was associated with type of degree earned (P=0.03) (Table 1).
Certainty and risk
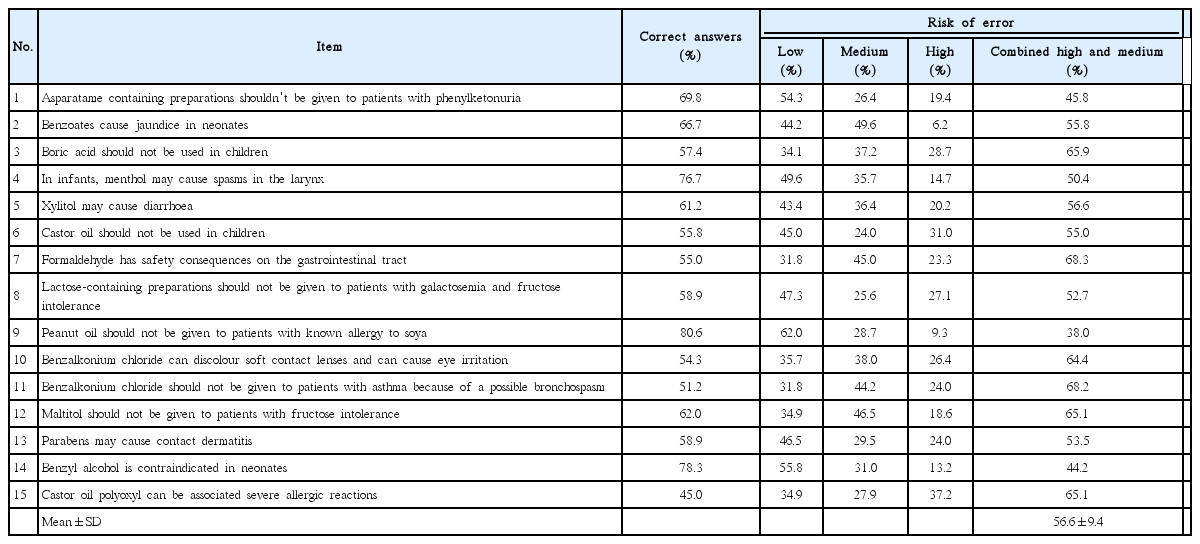
Pharmacists tended to be more certain of their answers when they gave correct answers as shown by the mean rank of certainty (Tables 3, 4). There was a positive correlation between the scores in APIs related questions and certainty scores as shown in Fig. 1. When high and medium risk of error were combined, there was higher risk of error (P<0.01) in questions related to excipients as compared to questions related to APIs. The risks of errors are shown in Tables 5 and 6. The overall knowledge level in both medications and pharmaceutical excipients among practicing community pharmacists was lower than expected (Table 1). Despite the generally insufficient knowledge, pharmacists had better knowledge in APIs than in pharmaceutical excipients (Table 2). Interestingly, scores of APIs test positively correlated with the certainty scores (Fig. 1A). However, no correlation was found between scores of pharmaceutical excipients test and certainty scores (Fig. 1B). Considering the mean rank for certainty scores, our results indicate that the pharmacists were generally certain of their correct answers in APIs related questions when they answer correctly (Table 3, Fig. 1A).
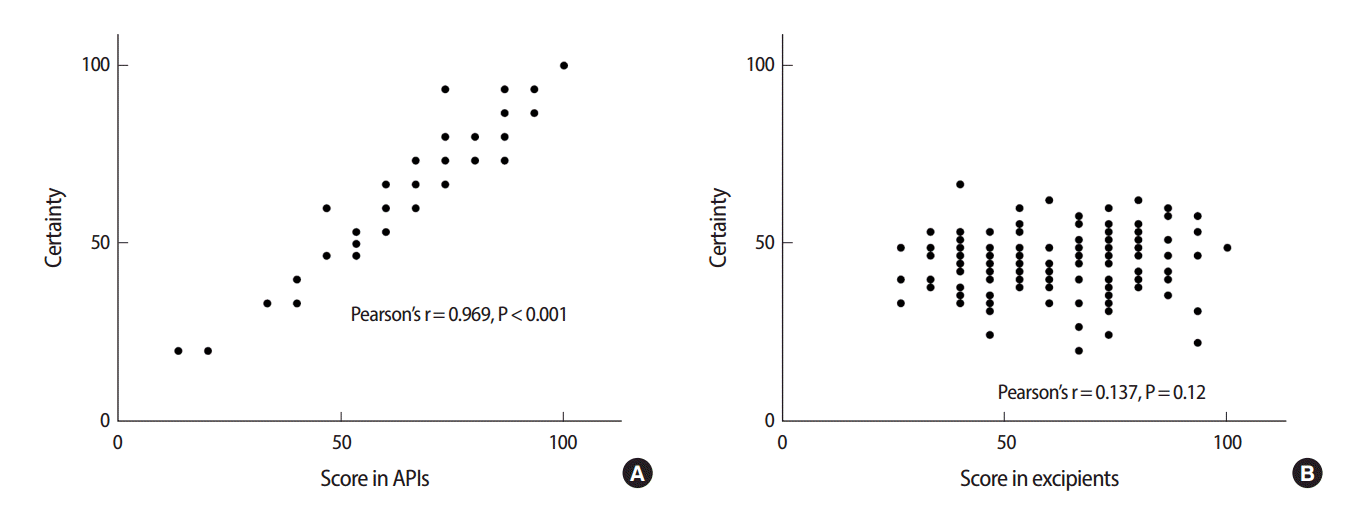
Correlation between knowledge scores and certainty for (A) APIs and (B) excipients related questions. APIs, active pharmaceutical ingredients.
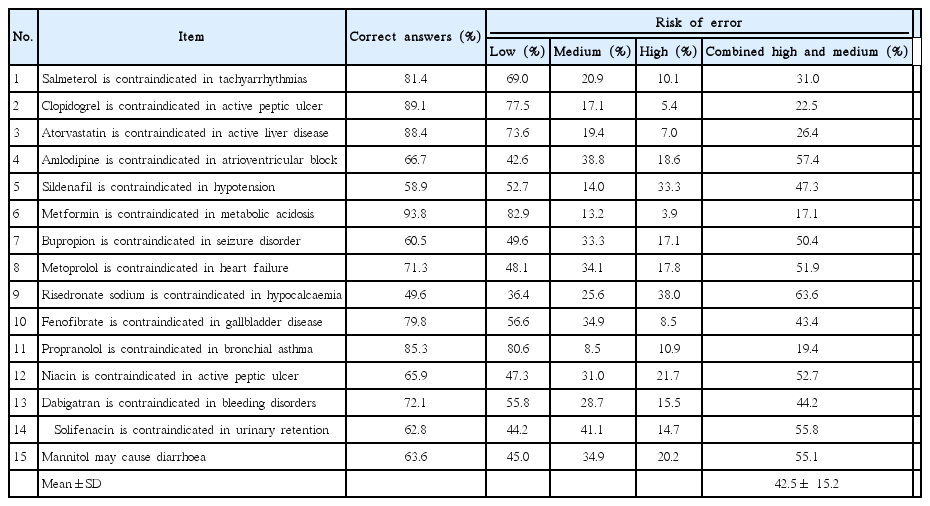
Results and distribution of risk of error for each item of test on active pharmaceutical ingredients
Discussion
The present study tested knowledge and self-rated certainty of community pharmacists on the adverse effects and contraindications of contents of pharmaceutical products. The study demonstrates that the knowledge of community pharmacists on the adverse effects and contraindications of APIs and pharmaceutical excipients was different. It showed that community pharmacists tended to have better knowledge on the adverse effects and contraindications of APIs than on pharmaceutical excipients. This insufficient knowledge might compromise the role of community pharmacists in providing optimal pharmaceutical care and prevention of medication errors.
Community pharmacists should have sufficient knowledge on the adverse effects and contraindications of medications in order to provide optimal pharmaceutical care [1]. Gold standards for sufficient knowledge on adverse effects and contraindications of APIs and pharmaceutical excipients are not available; hence, tests based on the learning goals of international core pharmacy curricula might be used as a standard [2]. Therefore, the test used in this study might serve as a standard to gauge knowledge on the adverse effects and contraindications of APIs and pharmaceutical excipients. Our results were consistent with those observed in a previous study conducted in the West Bank in which community pharmacists showed insufficient knowledge on the safe use of medications [3]. Different knowledge level on APIs and pharmaceutical excipients according to year of graduation or type of degree earned was similar to previous results which showed that enhanced medication knowledge was associated with obtaining postgraduate specialisations and experience [4].
In this study we included a self-rated certainty score for each question. The inclusion of this self-rated certainty score was to elucidate the connection between knowledge and risk of error in real life [4]. MCQs might be answered by some participants simply by guessing; however, inclusion of this self-rated certainty score could highlight the certainty or uncertainty of the answer given by each participant on each question. Findings of the present study showed that there were more medium and high risk of errors associated with items of pharmaceutical excipients test than items of APIs test (Tables 5, 6). This is particularly important since although physicians are responsible for safe prescribing, pharmacists have an important role in minimizing medication errors, especially those related to pharmaceutical excipients. Physicians receive training in pharmacology, therapeutics and safe prescribing; however, pharmacists are supposed to know better on the active and inactive ingredients composing the pharmaceutical products.
It is important to note that there is no clear definition of what constitutes sufficient knowledge on the adverse effects and contraindications of APIs and pharmaceutical excipients [2]; however, sufficient knowledge is essential to prevent medication errors, therefore, improving knowledge is essential for the optimal provision of pharmaceutical care.
The results of our study may be explained considering the following limitations. First, although we invited one pharmacist from each community pharmacy to participate in this study, the response rate was around 41%, which means that 59% of the invited pharmacists did not participate in the study. This might affect the external validity of our study. It could be overcome since our sample included participants from different age groups, genders, qualifications, and experience matching the overall population of pharmacists. Second, the risk of error was interpreted very conservatively as it might not be automatically transferable to medication errors in real life. Adding more conservation, we added the medium risk to the high risk for error in comparing scoring in APIs and pharmaceutical excipients.
In conclusion, community pharmacists included in this study showed a lack of adequate knowledge of side effects and contraindications of APIs and pharmaceutical excipients. Knowledge level was different according to qualification obtained and year of graduation. Lack of knowledge might negatively affect the role of community pharmacists in providing pharmaceutical care. There should be a policy to increase pharmacist knowledge on the adverse effects and contraindications of medications and pharmaceutical excipients by Palestine health authorities.
Notes
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Supplementary material
Audio recording of the abstract.